Nvidia SANA Inpainting
CodeInpainting implementation for Nvidia SANA [ICLR2025] using masked Flow scheduler
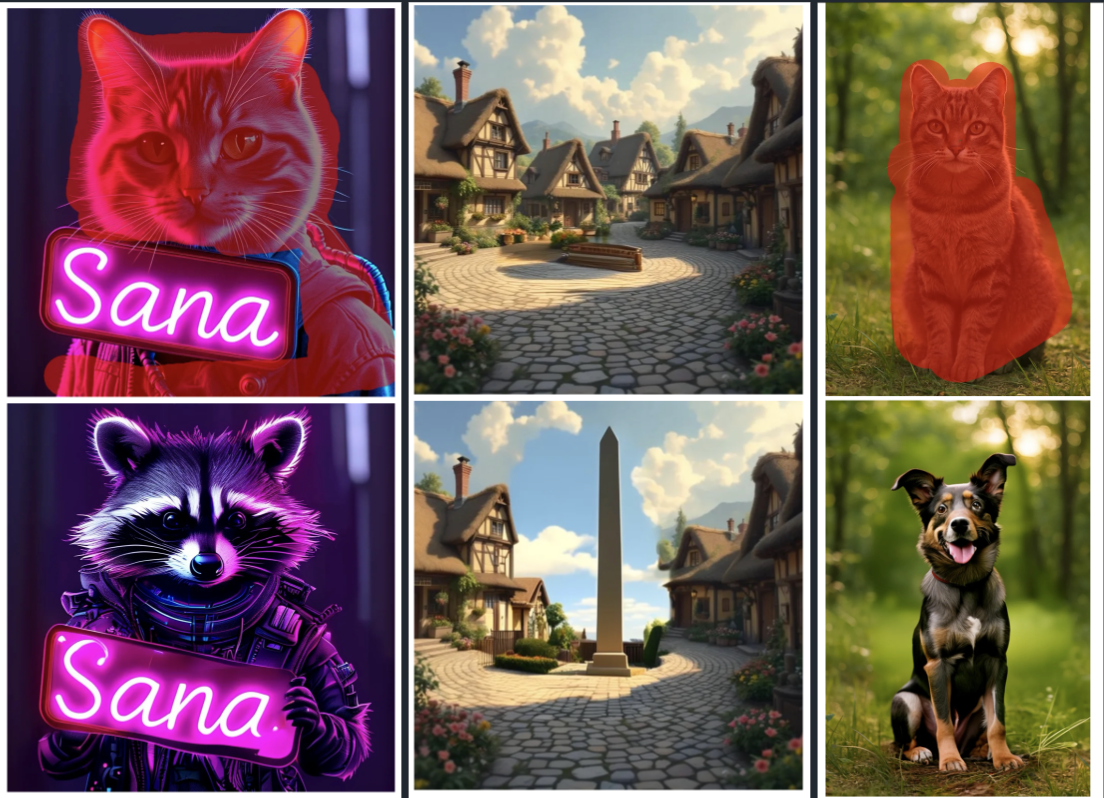

This project implements an inpainting capability, merged into the popular Nvidia SANA repository. It utilizes a masked version of the Flow scheduler, based on the Blended Latent Diffusion method [1], to enable inpainting without the need for additional fine-tuning or training.
Check out the merged PR here: SANA Pull Request #296
Overview
The implementation adds support for masking and inpainting directly within the SANA pipeline. It includes:
- Pipeline Implementation:
apps/sana_pipeline_inpaint.py - Application Logic:
apps/app_sana_inpaint.py - Gradio UI: A simple interface to load an image, draw a mask, and enter a prompt.
How it Works
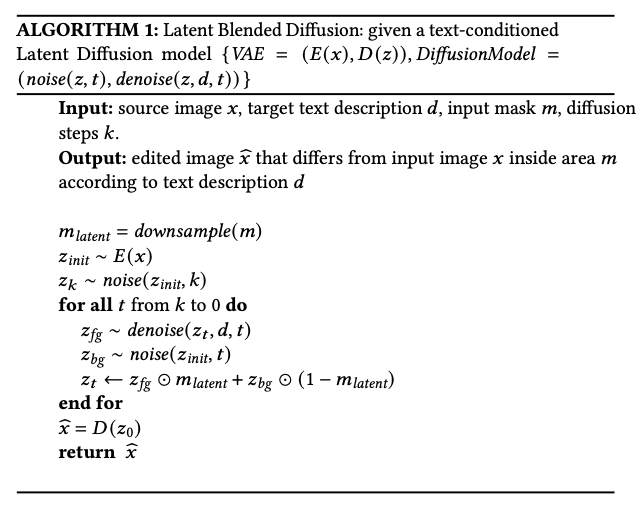
The method adapts the Flow scheduler to handle masks by utilizing the masked scheduling proposed in Latent Blended Diffusion (Avrahami et al., 2023). As illustrated in Algorithm 1 below, the process involves iterating through the diffusion steps and, at each step, blending the denoised latent (foreground) with the noisy latent of the original image (background) using the provided mask.
Specifically:
- The input mask is downsampled to the latent dimension ($m_{latent}$).
- The source image is encoded into the latent space ($z_{init}$) and noise is added to reach the starting noise level ($z_k$).
- During the denoising loop (from $t=k$ to $0$), the model predicts the foreground ($z_{fg}$) conditioned on the text prompt.
- Simultaneously, a background latent ($z_{bg}$) is generated by preserving the noise of the original image latent corresponding to the current timestep $t$.
- These two are composited: $z_t \leftarrow z_{fg} \odot m_{latent} + z_{bg} \odot (1 - m_{latent})$.
This ensures that the area outside the mask remains faithful to the original image, while the masked area generates new content based on the prompt.
Runtime: The process takes approximately 2x the time of standard image generation because inverse steps (or noise management) are required for the input image at each step to maintain consistency.
More Visualisations
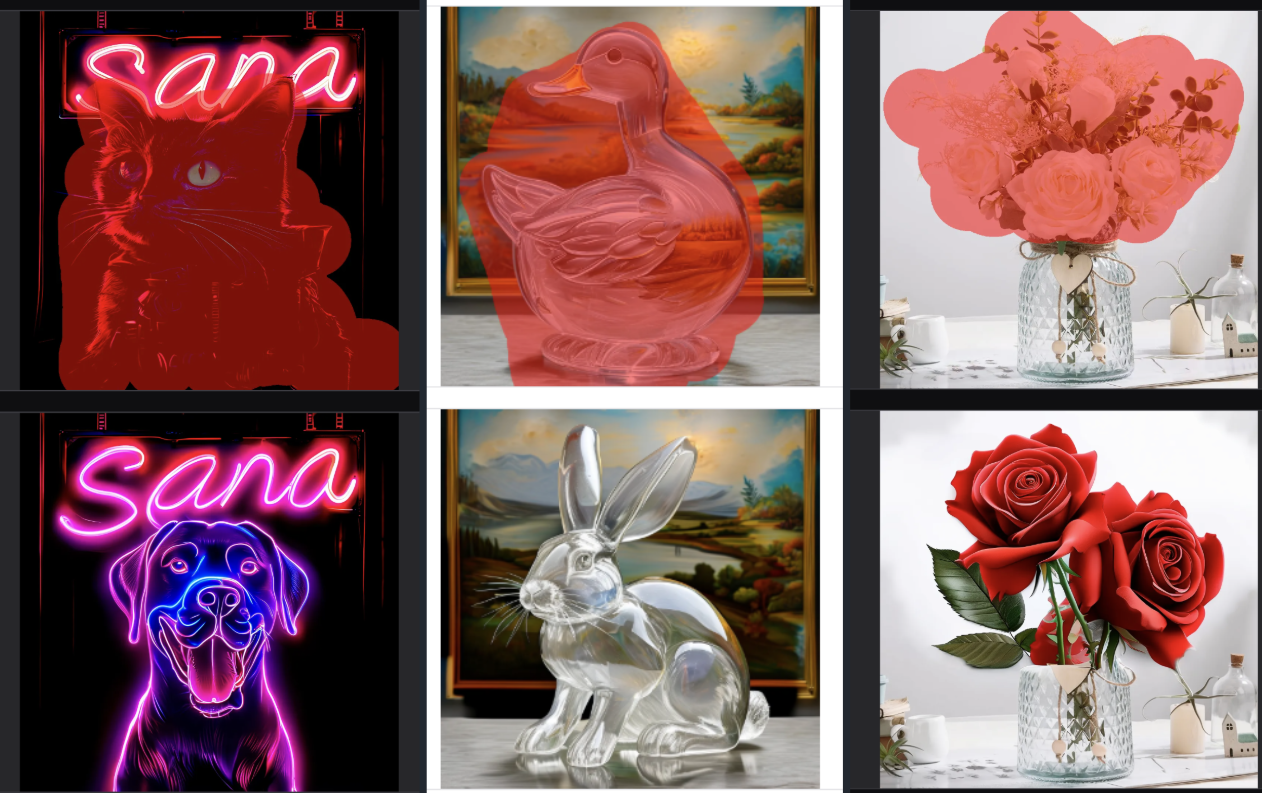
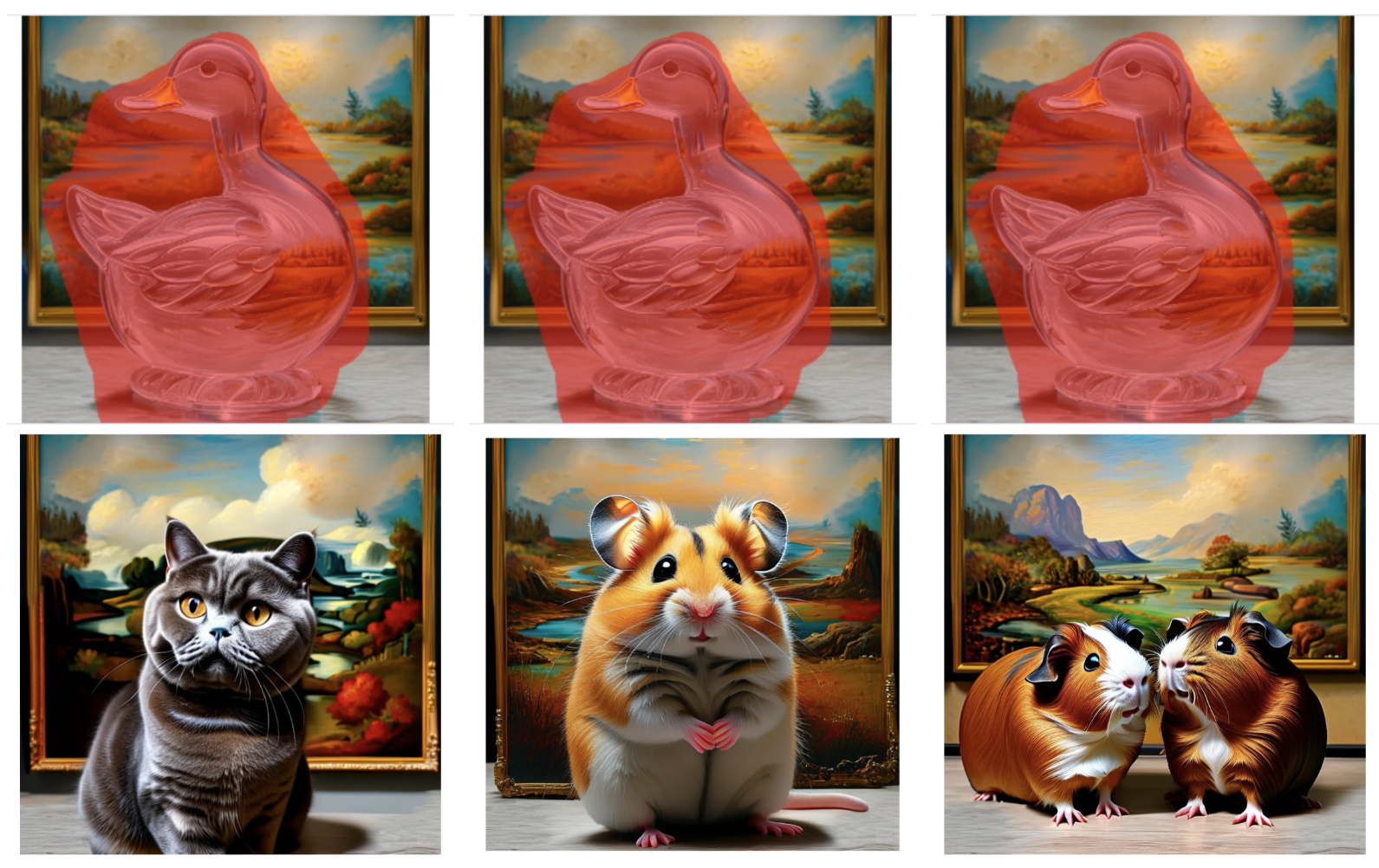


Limitations
- No Sana Sprint Support: Currently, this implementation does not support Sana Sprint due to the few-step scheduler degrading the blending results as naturally less blending steps can be performed.
- Mask Boundaries: The model lacks explicit knowledge of mask boundaries, which can be challenging in complex scenes or outdoor environments.
- Background Inpainting: Users may need to provide more detailed text prompts to guide the background generation effectively.
Usage
The project includes a Gradio UI for easy interaction. Users can upload an image, mask the area they want to modify, and provide a text prompt to guide the inpainting process.
python app/app_sana_inpaint.py
Considering that no fine-tuning or training is required, this approach offers a reasonable and accessible solution for inpainting with SANA.
References
- Avrahami, Omri, Ohad Fried, and Dani Lischinski. “Blended Latent Diffusion.” ACM Transactions on Graphics, vol. 42, no. 4, 2023, pp. 1-11, https://doi.org/10.1145/3592450.
- Xie, Enze, et al. “Sana: Efficient High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Linear Diffusion Transformers.” International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2025, https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.10629.