Fastai Course DL from the Foundations Train on Imagenette
Imagenette and Training our classifier (Lesson 5 Part 3)
#collapse
%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2
%matplotlib inline
#collapse
from exp.nb_10c import *
#collapse
path = Path("/media/cedric/Datasets/imagenette2-160/")
size = 128
tfms = [make_rgb, RandomResizedCrop(size,scale=(0.35,1)),np_to_float,PilRandomFlip()]
bs = 64
il = ImageList.from_files(path,tfms=tfms)
sd = SplitData.split_by_func(il,partial(grandparent_splitter,valid_name='val'))
ll = label_by_func(sd,parent_labeler,proc_y=CategoryProcessor())
ll.valid.x.tfms = [make_rgb,CenterCrop(size),np_to_float]
data = ll.to_databunch(bs,c_in=3,c_out=10,num_workers=8)
#collapse_show
def pass_through(x): return x
class Flatten(nn.Module):
def forward(self,x): return x.view(x.size(0),-1)
def conv(cin,cout,ks=3, stride=1,bias=False):
return nn.Conv2d(cin,cout,kernel_size=ks,stride=stride,padding=ks//2,bias=bias)
#collapse_show
activation = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def init_cnn(m):
if getattr(m,'bias',None) is not None : nn.init.constant(m.bias,0)
if isinstance(m,(nn.Conv2d,nn.Linear)): nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight)
for l in m.children(): init_cnn(l)
def conv_layer(cin,cout,ks=3,stride=1,zero_bn=False,act=True):
bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(cout)
nn.init.constant_(bn.weight,0. if zero_bn else 1.)
layers = [conv(cin,cout,ks,stride),bn]
if act : layers.append(activation)
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
#collapse_show
class ResBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,expansion,ni,nh,stride=1):
super().__init__()
nf,ni = nh*expansion,ni*expansion
#layers
#smaller nets
if expansion == 1 :
layers = [conv_layer(ni,nh,3,stride=stride),
conv_layer(nh,nf,3,zero_bn=True,act=False)]
#larger Nets ResNet-D Path A
else :
layers = [conv_layer(ni,nh,1),
conv_layer(ni,nh,3,stride=stride),
conv_layer(ni,nf,1,zero_bn=True,act=False)]
self.convs = nn.Sequential(*layers)
self.idconv = noop if ni == nf else conv_layer(ni,nf,1,act=False)
self.pool = noop if stride == 1 else nn.AvgPool2d(2,ceil_mode=False)
def forward(self,x): return act_fn(self.convs(x)+ self.idconv(self.pool(x)))
ResBlock Details
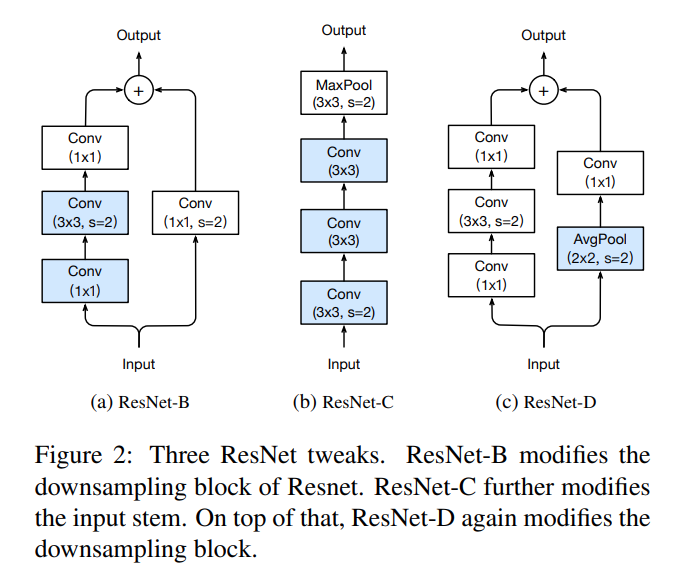
Batch Norm sometimes has weights of 0 and sometimes 1 during init. It allows us to init the Conv branch to 0 and the identity mapping to 1. The gradient won't explode that way.
ResNet 50 and onwards use 3 convs, smaller ones use 2. They also use Bottleneck layers (64 filters-> 16filters -> 64 filters), the normal block for larger ResNets. ResNet-D also uses downsample to make sure the two branches can be added. So when stride is not 1, and AvgPool layer with stride of 2 is deployed for different grid size, and 1x1 conv to change the number of filters (if not equal).
#collapse_show
class XResNet(nn.Sequential):
@classmethod
def create(cls,expansion,layers,c_in = 3,c_out=1000):
nfs = [c_in,(c_in+1)*8,64,64]
stem = [conv_layer(nfs[i],nfs[i+1],stride=2 if i==0 else 1)
for i in range(3)]
nfs = [64//expansion,64,128,256,512]
res_layers = [cls._make_layer(expansion,nfs[i],nfs[i+1],
n_blocks=l,stride=1 if i==0 else 2)
for i,l in enumerate(layers)]
res = cls(*stem,nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3,stride=2,padding=1),*res_layers,
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1),Flatten(),nn.Linear(nfs[-1]*expansion,c_out))
init_cnn(res)
return res
@staticmethod
def _make_layer(expansion,ni,nf,n_blocks,stride):
return nn.Sequential(*[ResBlock(expansion,ni if i==0 else nf,nf,stride if i==0 else 1)
for i in range(n_blocks)])
#collapse_show
def xresnet18 (**kwargs): return XResNet.create(1, [2, 2, 2, 2], **kwargs)
def xresnet34 (**kwargs): return XResNet.create(1, [3, 4, 6, 3], **kwargs)
def xresnet50 (**kwargs): return XResNet.create(4, [3, 4, 6, 3], **kwargs)
def xresnet101(**kwargs): return XResNet.create(4, [3, 4, 23, 3], **kwargs)
def xresnet152(**kwargs): return XResNet.create(4, [3, 8, 36, 3], **kwargs)
#collapse_show
cbfs = [partial(AvgStatsCallback,accuracy), ProgressCallback, CudaCallback,
partial(BatchTransformXCallback, norm_imagenette),
# partial(MixUp, alpha=0.2)
]
#collapse_show
loss_func = LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy()
arch = partial(xresnet18, c_out=10)
opt_func = adam_opt(mom=0.9, mom_sqr=0.99, eps=1e-6, wd=1e-2)
#collapse_show
def get_batch(dl, learn):
learn.xb,learn.yb = next(iter(dl))
learn.do_begin_fit(0)
learn('begin_batch')
learn('after_fit')
return learn.xb,learn.yb
We need to replace the old model_summary since it used to take a Runner.
#collapse_show
def model_summary(model, data, find_all=False, print_mod=False):
xb,yb = get_batch(data.valid_dl, learn)
mods = find_modules(model, is_lin_layer) if find_all else model.children()
f = lambda hook,mod,inp,out: print(f"====\n{mod}\n" if print_mod else "", out.shape)
with Hooks(mods, f) as hooks: learn.model(xb)
#collapse
learn = Learner(arch(), data, loss_func, lr=1, cb_funcs=cbfs, opt_func=opt_func)
#collapse
learn.model = learn.model.cuda()
model_summary(learn.model, data, print_mod=False)
#collapse
arch = partial(xresnet34, c_out=10)
#collapse
learn = Learner(arch(), data, loss_func, lr=1, cb_funcs=cbfs, opt_func=opt_func)
#collapse
learn.fit(1, cbs=[LR_Find(), Recorder()])
#collapse
learn.recorder.plot(3)
#collapse_show
def create_phases(phases):
phases = listify(phases)
return phases + [1-sum(phases)]
#collapse_show
print(create_phases(0.3))
print(create_phases([0.3,0.2]))
#collapse_show
lr = 1e-2
pct_start = 0.5
phases = create_phases(pct_start)
sched_lr = combine_scheds(phases, cos_1cycle_anneal(lr/10., lr, lr/1e5))
sched_mom = combine_scheds(phases, cos_1cycle_anneal(0.95, 0.85, 0.95))
#collapse_show
cbsched = [
ParamScheduler('lr', sched_lr),
ParamScheduler('mom', sched_mom)]
#collapse_show
learn = Learner(arch(), data, loss_func, lr=lr, cb_funcs=cbfs, opt_func=opt_func)
#collapse_show
learn.fit(5, cbs=cbsched)
#collapse_show
def cnn_learner(arch, data, loss_func, opt_func, c_in=None, c_out=None,
lr=1e-2, cuda=True, norm=None, progress=True, mixup=0, xtra_cb=None, **kwargs):
cbfs = [partial(AvgStatsCallback,accuracy)]+listify(xtra_cb)
if progress: cbfs.append(ProgressCallback)
if cuda: cbfs.append(CudaCallback)
if norm: cbfs.append(partial(BatchTransformXCallback, norm))
if mixup: cbfs.append(partial(MixUp, mixup))
arch_args = {}
if not c_in : c_in = data.c_in
if not c_out: c_out = data.c_out
if c_in: arch_args['c_in' ]=c_in
if c_out: arch_args['c_out']=c_out
return Learner(arch(**arch_args), data, loss_func, opt_func=opt_func, lr=lr, cb_funcs=cbfs, **kwargs)
#collapse_show
learn = cnn_learner(xresnet34, data, loss_func, opt_func, norm=norm_imagenette)
#collapse_show
learn.fit(5, cbsched)
You can see all this put together in the fastai imagenet training script. It's the same as what we've seen so far, except it also handles multi-GPU training. So how well does this work?
We trained for 60 epochs, and got an error of 5.9%, compared to the official PyTorch resnet which gets 7.5% error in 90 epochs! Our xresnet 50 training even surpasses standard resnet 152, which trains for 50% more epochs and has 3x as many layers.